Trace flags are used to temporarily set specific server characteristics or to switch off a particular behavior. They are usually scoped to a global level or a session only level. For this blog post I thought it would be handy to show you how to enable (and disable) global based trace flags and then check the status on your system.
The difference between global and session is important to understand, global trace flags are visible to every connection whereas session scoped means that the trace flag is visible to only that connection.
Global Scope
For this example I will be using a global trace flag that overrides the use of index hints (This is not something I do or encourage; it is just a use case for this post).
SELECT AddressID,city FROM [Person].[Address] WHERE City = 'Albany'
I wrote a basic query because as you will see it gives me a Non-Clustered Index Seek.

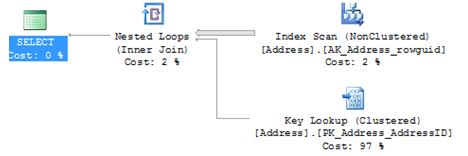
I am now going to write a query where I will force the above SELECT statement to use an index where it really shouldn’t – the outcome is a scan with a key lookup – yep not what we want
SELECT AddressID,city FROM [Person].[Address] WITH (INDEX (AK_Address_rowguid)) WHERE City = 'Albany'
So let’s set a global based trace flag to say for any connection ignore ALL index hints. I would expect it to go back to an index seek. The -1 in the TRACEON is very important – that is what makes it global.
DBCC TRACEON (8602,-1) SELECT AddressID,city FROM [Person].[Address] WITH (INDEX (AK_Address_rowguid)) WHERE City = 'Albany'

So it’s clear to see that even with the index hint it is now ignored.
Because it’s global I then connected to the server as someone else and issued the query with the same results.
Check status
To check what trace flags are enabled on the system run the below.
DBCC TRACESTATUS (-1); GO

Turn off
DBCC TRACEOFF (8602,-1) DBCC execution completed. If DBCC printed error messages, contact your system administrator. DBCC TRACESTATUS(-1); GO
Re-issuing the above DBCC TRACESTATUS will now show nothing.
What about after a restart?
I switched the trace flag back on then restarted SQL Service and issued the status command:

DBCC TRACESTATUS(-1); GO
DBCC execution completed. If DBCC printed error messages, contact your system administrator.
The flag has been lost.
SQL Server Configuration Manager
Personally I prefer using configuration manager if I am using trace flags. Under properties of your MSSQLSERVER you will see a start-up parameters tab.

Click ADD.

After you have restarted logon to the SQL Server and check the status
DBCC TRACESTATUS(-1); GO
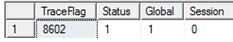
I restarted the SQL service again just to prove that settings will be preserved – which they are and that is the part that I like about configuration manager.

Pingback: SQL Server – Playing With Trace Flags - SQL Server Blog - SQL Server - Toad World