A really quick one today, something that made me think for a minute and I thought it might make others think too. So you have enabled TDE – Transparent Data Encryption (you can see these previous posts here: https://blobeater.blog/?s=tde&submit=Search) on your SQL Server database and in the back of your mind you know TempDB gets encrypted too.
Tag Archives: TSQL
SQL Server Memory Metrics
A very quick post for today, recently I have been working on some code to gather metrics around SQL Server memory, more specifically, how much memory is on your server, your total / target memory and PLE. (If you want to know more about total vs target see this link: https://blobeater.blog/2017/03/01/sql-server-target-vs-total-memory/)
Find when your SQL Server database grew
A quick post that is hopefully useful, I wanted a quick way to find the time, size of the database file size change and who caused it.
Using Extended Events in Azure
Over the past 6 months I have been trying to push myself to use extended events (XEvents) over SQL trace, once you get past the learning curve it’s probably the way to go. If you are operating in the Azure space then you have no choice. Extended events are what you will need to use if you want to collect information against SQL database. There are some subtle differences on how you write the T-SQL between SQL database (Azure) and your locally installed SQL Servers.
Checking Time Zones in SQL Server
I was building some basic queries around time zone manipulation and I am happy to say that I enjoyed myself as I found a way to get a time based on a geographic region.
This new feature is available to you from SQL 2016 which obviously means SQL database too (Azure). It is called AT TIME ZONE.
AT TIME ZONE implementation relies on following registry hive where time zones are installed: KEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Time Zones. This is exposed via the following query
SELECT * FROM sys.time_zone_info
Looking at books on line via https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/mt612790.aspx it is wrong.
Look at the screen shot, it states it is supported from SQL 2008 – well it is not, it only works on 2016.

Running it on a non SQL 2016 server you will get the following message:
Msg 208, Level 16, State 1, Line 1 Invalid object name ‘sys.time_zone_info’.
On a correct SQL version it will return the following. (Snippet)
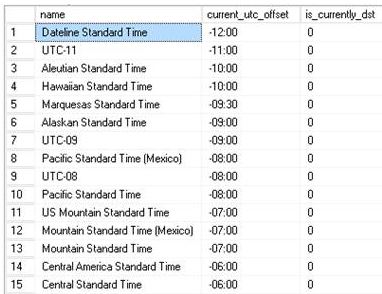
This information is key as we will use it to build the time zone queries (which is very basic).
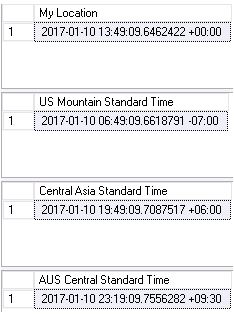
SELECT SYSDATETIMEOFFSET() AT TIME ZONE 'GMT Standard Time' AS [My Location] GO SELECT SYSDATETIMEOFFSET() AT TIME ZONE 'US Mountain Standard Time' AS [US Mountain Standard Time] GO SELECT SYSDATETIMEOFFSET() AT TIME ZONE 'Central Asia Standard Time' AS [Central Asia Standard Time] GO SELECT SYSDATETIMEOFFSET() AT TIME ZONE 'AUS Central Standard Time' AS [AUS Central Standard Time]
Based on the zone offset you will get the relevant correct time.